ACL Injury and Methods to Reduce the Damage
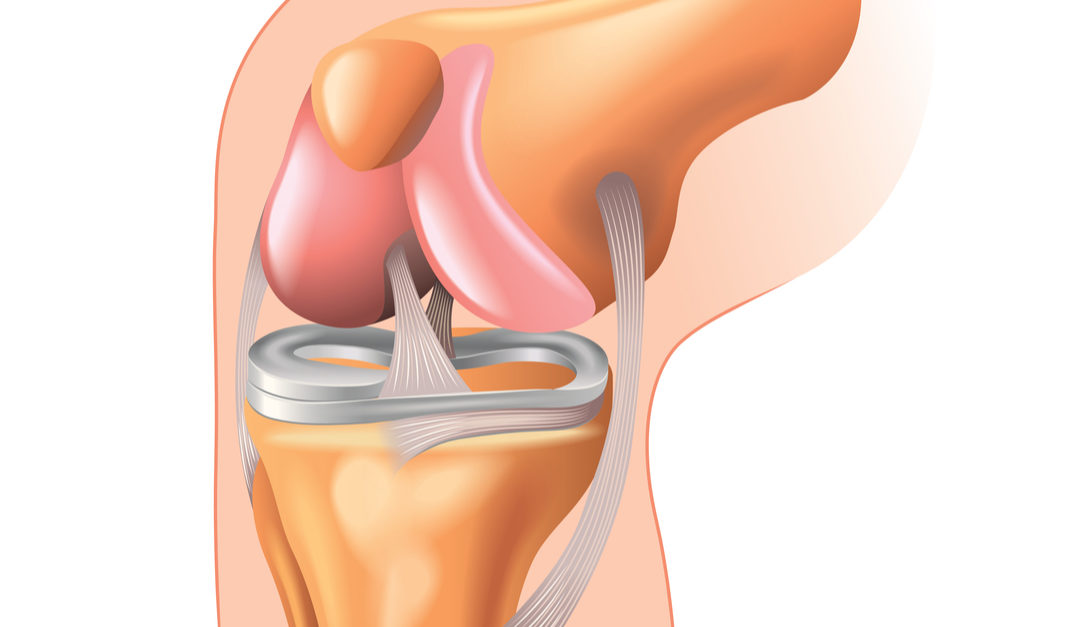
Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) injuries are a common type of knee disturbance sports persons undergo. However anybody can go through an ACL injury, this type of disturbance is related with athletes because it is caused by a fast halt movement which tends to occur more in modest activity than in day to day lifestyle.
The cruciate tendon is found inside the knee joint and many ACL injuries consequence with a full scratch. It’s also likely to injure your ACL to changing amounts. This means the muscle has become movable, although it’s still connected. It depends on the degree of the sprain; the knee can continue mostly steady. For those who do not play on the go sports, the wound might be treated with treatment or invigorating. In a case of a full rip, the muscle will not renovate itself. The only process to recover the knee to the point where the complete gesture is achievable with the help of surgery.
10 Facts about ACL Injuries
Osteoarthritis Risk: Around 50% of those with an ACL injury will grow osteoarthritis in recent years.
Higher Risk for Women: Female players get a higher proportion of risk for this injury than their male equivalents due to augmented lumbar angles placing more pressure on the knees.
Collateral Damage: Around 50% of those with ACL damage also have an injury to a tendon or other muscles in the knee.
Surgical Recommendation: Surgery treatment is highly recommended for most ACL injuries when there is an amalgamation of wounds. A full tear in the ACL will not treat without surgery.
Higher Risk Sports: Football, soccer, and basketball entire one will get a higher risk of ACL injury, with other sports persons and non-athletes can undergo this injury.
Non-Contact Doesn’t Reduce Risk: Around 70% of ACL injuries were continuous in non-contact sports while only 40% are accredited to contact sports.
Preemptive Training: Preemptive training programs are reported to diminish knee injuries like ACL by as much as 60%.
Daily Training: For preventive training to be most effective, it is highly recommended that players retain a daily schedule of these workouts at least 2 or 3 times every week.
Exercises to Stop Injury: Preemptive training workouts comprise strength, proprioception and bio feedback training. A correct loosening up may take as just as 10 or 15 minutes and as extended as one hour for a complete preemptive training period.
Benefits in Preventative Training
Preventative training workouts don’t simply reduce the risk of an ACL injury; they also recover the athlete’s performance level. Sports persons who retain a day to day schedule of preventative training also progress their skills in hurry speed and aerobic fitness.
